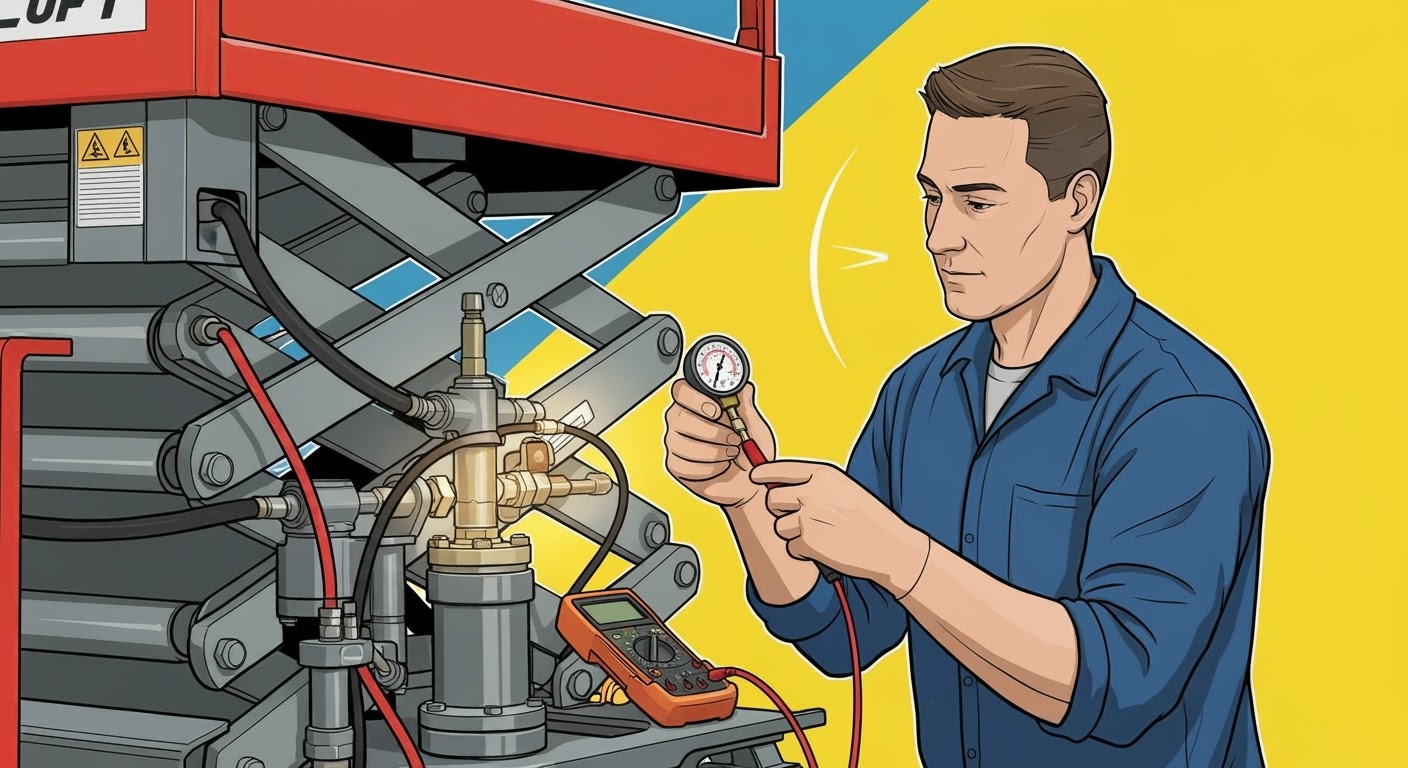
Hydraulic Pump Symptoms in Scissor Lifts:
Hydraulic pumps are like the blood of a scissor lift. They are the ones that transfer any power from the liquid to the mechanical motion that brings the platform up and down. If the hydraulic pump breaks, a scissor lift may not be used, and it can be dangerous, as well as a loss of time. Hence, it is more prominent to understand the hydraulic pump symptoms and its failures and rectify before more damage occurs.
Importance of Hydraulic Pump Symptoms – Hydraulic Failure in Scissor Lifts:
The identification of the early symptoms of the pump’s breakdown, the availability of beginner-friendly repair methods, and the knowledge of the ways for fleet managers and operators can headline and the long life of equipment.
With the advice and experience of specialists in the field, this article will explore the warning signals of hydraulic pump symptoms and its failure, sketch out reputable resolutions, as well as introduce various upgradation strategies designed to strengthen reliability and productivity. You should not overlook the regular maintenance of the hydraulic system if you need it to function without failure and remain safe.
Because if you ignore the hydraulic pump symptoms, which is the part that raises and lowers the platform, you might experience a poor performance or even a breakdown.
Understanding Hydraulic Pump Symptoms in Scissor Lifts
Hydraulic pumps in scissor lifts are those which are responsible for generating the fluid pressure necessary to drive the lift cylinders. Basic knowledge of how they work, their various types, and the key elements gives the way to finding fault and executing maintenance that works.
From the fixed-displacement gear pumps to the variable-displacement axial piston pumps, each design has characteristics peculiar to itself that have an impact on the performance, efficiency, and the time between services.
Pump Types and Configurations:
- Fixed-displacement gear pumps are used only when the flow rate is required to be constant and the pump should be very simple and strong at the same time.
- Variable-displacement axial piston pumps are the kind of pumps that not only offer variable flow but also pressure for some energy savings.
- Tandem pump setups are the perfect decision in case the main lift and the auxiliary functions are needed to be performed by different pump stages.
Key Components:
- Housing and Rotors: They protect the moving parts and create the passages for the fluid that drives the turbine.
- Seals and Bearings: Seals make the parts both stationary and rotating tight and Bearings give the rotating pair support during the high hydraulic pressures.
- Pressure Relief Valves: In a situation of an unnecessary pressure rise, these valves discharge the fluid to keep the system without risk.
Operational Principles:
- Pascal’s Law Application: Fluid pressure is transmitted through a liquid to all directions which in turn, allows the small input forces to give the large output forces.
- Flow Control: By the means of the pump displacement regulation or using the external valves, the system gains control of the lifting speed.
- Cavitation Awareness: As a result of the inlet pressure below the fluid’s vapor pressure, the micro-bubbles occur and these micro-bubbles harm the parts.
Understanding these conduits of knowledge empowers technicians to compare visual hydraulic pump symptoms to certain pump malfunctions, thereby directing repairs straight to the target and hence saving the company from costly breakdowns, time, and labor.

Hydraulic Pump symptoms and Its Failure Causes
In the initial stages, the identification of faults in hydraulic pumps could help to save a large amount of repair cost. It also enables a reduction in the time of operation (downtime). Users should be cautious to spot these strange activities that come with almost all pump malfunctions and if not early intervention is taken it may get serious or the pump will be damaged deeply.
Slow or Erratic Platform Movement:
- Solid indication that the lift is responding sluggishly or is hesitating is a sign of poor fluid flow or internal leakage.
- Variable displacement pumps may cause incorrect speed adjustments, resulting in speed inconsistencies.
Strange Noises and Vibrations:
- Noise that sounds like knocking or banging, or air leak tells us that there is air inside the unit or that internal components are declined.
- Too high a voice and a lot of vibrations indicate either the wear of the bearing or rotor misalignment.
Visible Fluid Leaks:
- If the hydraulic fluid is piled around the pump housing or the hoses, the seal probably has broken.
- External leaks are bad because they bring in impurities, and they also this way further intensify wear.
Overheating of Hydraulic Oil:
- The possibility of the oil reaching too hot levels shows that the internal parts are being damaged, resulting in having much friction.
- Oil quality lowers as it becomes more and thicker, and this will affect the efficiency of the pump even more.
Pressure Drop and Loss of Holding:
- The platform may continue to move down under load due to the malfunction of the relief valve or internal bypassing.
- When a relief valve chatter is heard, there might be a pump failure that is around the corner.
Correctly identifying these issues early — before a disaster strikes, which makes it possible for maintenance teams to arrange repairs without disrupting service, operations.
Typical Solutions for Hydraulic Pump Symptoms Problems
Once the hydraulic pump symptoms are uncovered, quick systematic troubleshooting and repair operations can bring back the pump to life. The following repairs cover the most common malfunctions:
Check and Refill Hydraulic Fluid:
Make sure you check the container and then add the recommended hydraulic fluid to the right level of the reservoir to keep the hydraulic oil and its viscosity.
If you are not sure how the oil is, then get a sample of the fluid, analyze it and replace it with new one if it has changed its consistency and is very annoying to you if it contains strange particles.
Bleed Air from the System:
Keep the highest points of the pump open by slightly unscrewing the air bleed valves so that the air can escape when the system is not engaged.
Once the lift has completely worked, air bubbles or cavitation noises will also disappear, meaning the air pockets are removed.
Replace Seals and O-Rings:
First of all, you need to uncover the pump drive to be able to get to the sealing, which in case lost their elastic properties over time or failed to resist the impacts of usage.
Go for seal kits specially manufactured for this occasion in order to avoid disharmony between the gaskets and the exposed valve parts and to enjoy usage for longer periods of time.
Repair or Replace Pressure Relief Valves:
Thoroughly clean spring and valve seat surfaces; then after visual inspection, change the items hence, if they are dirty or corroded, that may become the reasons for the wide-open condition of your relief valve.
Set pressures to the convince of the manufacturers to avoid lockout from excessive current.
Rebuild or Swap the Pump Unit
Make an internal investigation for possible damage by the usage of a certain tool and if gears, vanes or pistons have any signs of creases or excessive wear.
If the damage is minor, only rebuild the pump, while in the case of serious components wear, new pump installation is the best course of action.
Stay ahead of time with these scheduled events that are triggered with the number of work hours and type of load, and these actions can lead to reducing the risk of system failure.
Upgrade Options for Hydraulic Systems
Modification of hydraulic circuit can do a lot to the reliability, efficiency, and safety of the worker. The following tips will be helpful while setting up equipment overhaul:
Variable-Displacement Pump Retrofit:
The new pump provides a wide range of flows that can be adjusted to the demand instantly, thus reducing electricity consumption significantly.
Increases the precision of lifting speeds and diminishes heat production.
High-Efficiency Filtration Systems:
Embeds the filters right before the pump that absorb the possible irregularities of a micro-scale particle and protect the pump from wear.
Lengthens the oil duration in the system and minimizes the replacement of the fluid.
Enhanced Cooling Solutions:
Equips the system with additional heat exchangers or larger ones so that the fluid temperature remains consistent even under harsh mechanical duty conditions.
Averts liquid viscosity degradation and pump erosion caused by cavitation.
Electronic Pump Control Modules:
The system is smart as it is equipped with both sensors and machines to track the temperature, the flow, the pressure of the fluid, the monitoring process goes in real-time mode.
Gives an early warning through an online monitoring system for predictive maintenance.
Seal and Material Upgrades:
Employs implementation of synthetic materials in the formulation of seals that are reinforced with stainless steel to combat wear and tear as well as chemical attack. Once the hydraulic pump symptoms are identified strengthens pump longevity for use in environments prone to abrasion and corrosion.
Upgrade Comparison Table
| Upgrade Option | Description | Benefits | Approx. Cost (USD) |
| Variable-Displacement Pump Retrofit | Replaces fixed pump with control-adjustable unit | Energy-saving, smoother operation | 2,500–4,000 |
| High-Efficiency Filtration | Adds micron-rated filters inline with pressure circuit | Reduces wear, extends oil change intervals | 300–600 |
| Enhanced Cooling System | Installs larger or additional oil coolers | Maintains viscosity, prevents overheating | 800–1,200 |
| Electronic Control Module | Digital monitoring with alarm outputs | Predictive maintenance, safety alerts | 1,200–2,000 |
| Advanced Seal & Material Package | Upgrades to PTFE seals and hardened components | Longer life, chemical resistance | 400–700 |
By choosing these upgrades tailored to perfection for workload and environmental conditions, operators can effectively and dramatically reduce downtime along with maintenance costs while optimizing scissor lift performance efficiently and can identify hydraulic pump symptoms in early stage.
Final Share Of The Hydraulic Pump Symptoms in Scissor Lifts
A hydraulic pump that is in good working condition is critical for the safe, dependable, and energy-efficient operation of scissor lifts. By being aware of the design of the pump, noticing the early indications of failure, performing targeted repairs, and opting for strategic system upgrades, operators can make the lives of the machines longer and reduce the cost of repairs. Operators, who adhere to the above-mentioned maintenance practice, can thus maximize the serviceable life of the equipment and at the same time avoid expensive repairs that might result from unexpected pump failures.
- Early Diagnosis Saves Costs: Consistent examination ensures that small problems become known before they become serious pump failures.
- Proactive Repairs Extend Lifespan: If a seal is broken, a valve is not properly adjusted, or air is trapped in the system, a relatively small and easy repair is enough to avoid the extensive work of fixing a major failure.
- Smart Upgrades Boost ROI: This move involves making an investment in variable-displacement pumps and optionally adding more effective filtration so as to ensure lower energy consumption is achieved along with less system breakdowns.
Implement a thorough hydraulic maintenance program on a regular basis and being proactive with your prompt repairs and system upgrades will allow you to have operational and trouble-free scissor lifts for years to come.
FAQ’s:
What are the reasons for a hydraulic pump symptoms to fail in a scissor lift?
A hydraulic pump fails quickly because of various reasons such as; having low fluid levels, air entering, and deterioration of the seal, and not forgetting the contamination and cavitation causes.
How do I bleed air from my scissor lift’s hydraulic system?
Widen the opening of the highest points of the pump until the airflows out without bubbles when the lifting is activated or shut gently, then the air will be reduced.
Can I do the refurbishing of the hydraulic pump that I possess instead of replacing it?
As a user, you can easily repair and use the same hydraulic pump again in place of acquiring a new one provided that the hydraulic pump is only worn out in the seals and therefore a minor scoring can also be repaired through a rebuild kit.
How often should hydraulic fluid be changed?
Check your owner’s manual for the manufacturer’s recommendation, which is usually every 1,000-2,000 hours of operation. If a fluid analysis shows high levels of dirt, change the fluid sooner.
What are the advantages of a variable-displacement pump considering an upgrade?
Upgrading to a variable pump is a sure way to save power and reduce heat besides the more important advantage of control over lifting speeds.
How can I prevent cavitation in my hydraulic system?
Make sure that there is a correct level of the fluid. Proper viscosity oil should be used, inlet filters should be kept clean, and lastly, try using no restrictive intakes.
Is it worth installing electronic monitoring on older lifts?
Of course, it is—electronic modules offer real-time information, early warnings of maintenance, and also, the lifespan of the pump is lengthened significantly, thus it is a profitable investment.